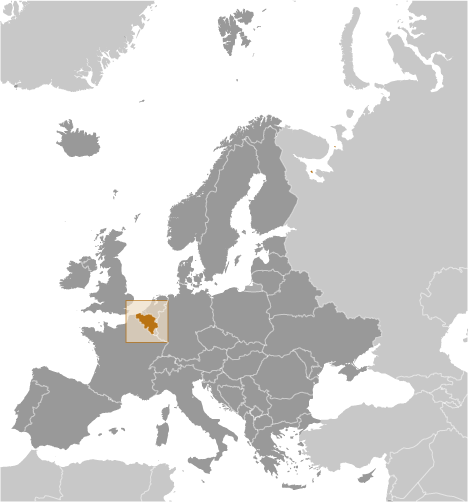
Belgium is a Western European country occupying an area of 30,689 km2 (11,849 sq mi).
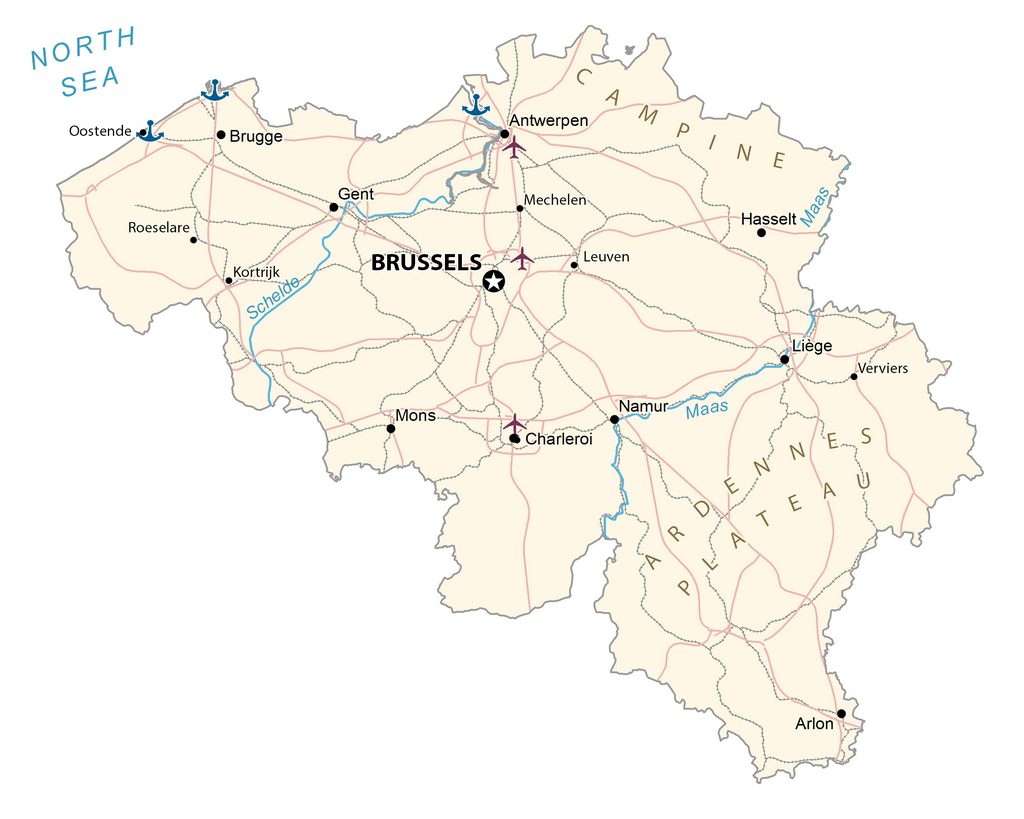
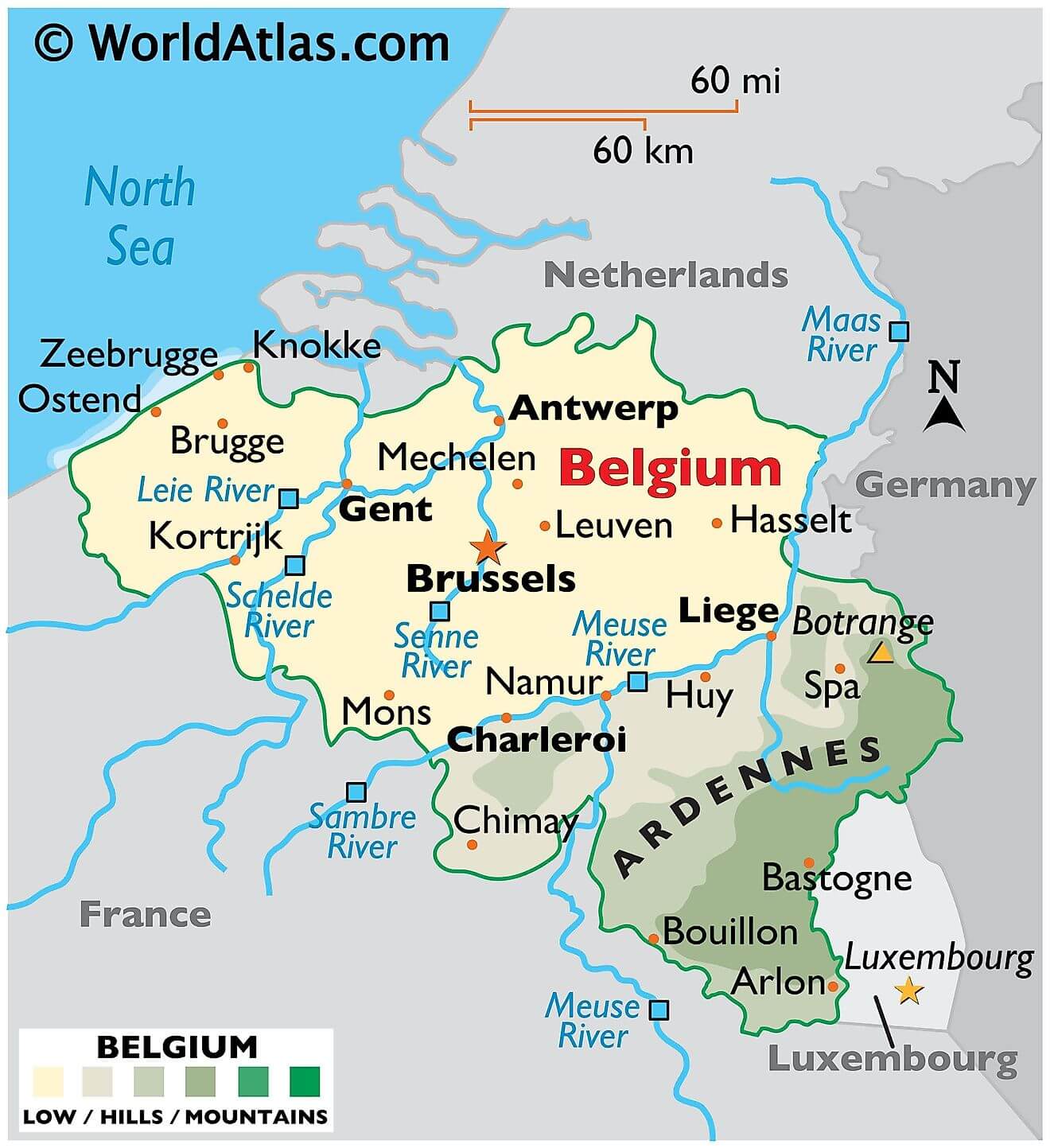
As can be observed on the physical map of Belgium there are three main geographical regions to Belgium: the coastal plain to the northwest, the central plateau, and the Ardennes uplands to the southeast. A small area called the Paris Basin is used to refer to the southernmost tip of the country.
The coastal area is a series of sandy beaches and polders, backed by protecting dunes. Inland, up to the Meuse River, the land is generally flat, with numerous canals and dikes protecting the land from the sea. It’s crisscrossed by many small tributaries of the Schelde River. Valleys, caves and small gorges can also be found in this area.
East of the Meuse, forested hilly conditions rise to the rugged and flat-topped mountains of the Ardennes Region. The highest point is the Botrange, at 2,276 ft. (694m). A yellow triangle marks the position of this point on the map.
All rivers and streams of Belgium drain into the North Sea except for the Oise River that empties into the English Channel. The Scheldt, Meuse, and Yser are the three major rivers of the country. The country also has several lakes like Lake Genval, Lake Gileppe, Lake Eupen, Lake Robertville, etc.
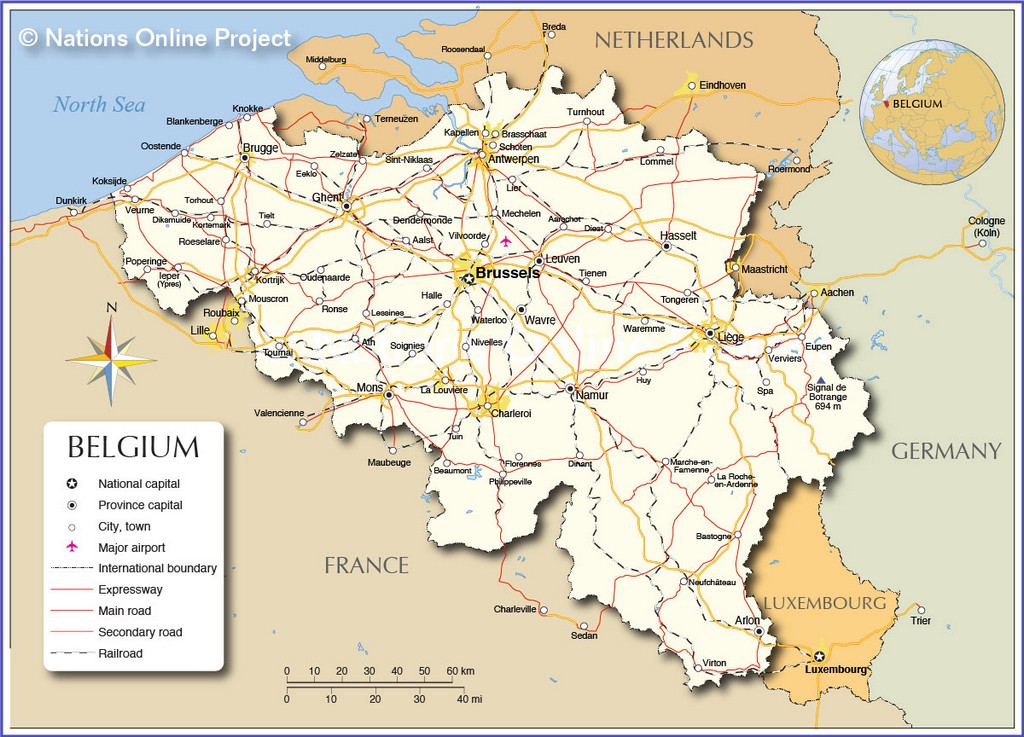
Belgium is a beautiful country located in the heart of Western Europe. From its low coastal plain in the north to its plateaus and Ardennes Upland region to the southeast, the country is filled with stunning physical features. This map of Belgium showcases its major cities, rivers, and highways, along with a satellite and elevation map to help you explore its diverse landscape.
Online Interactive Political Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
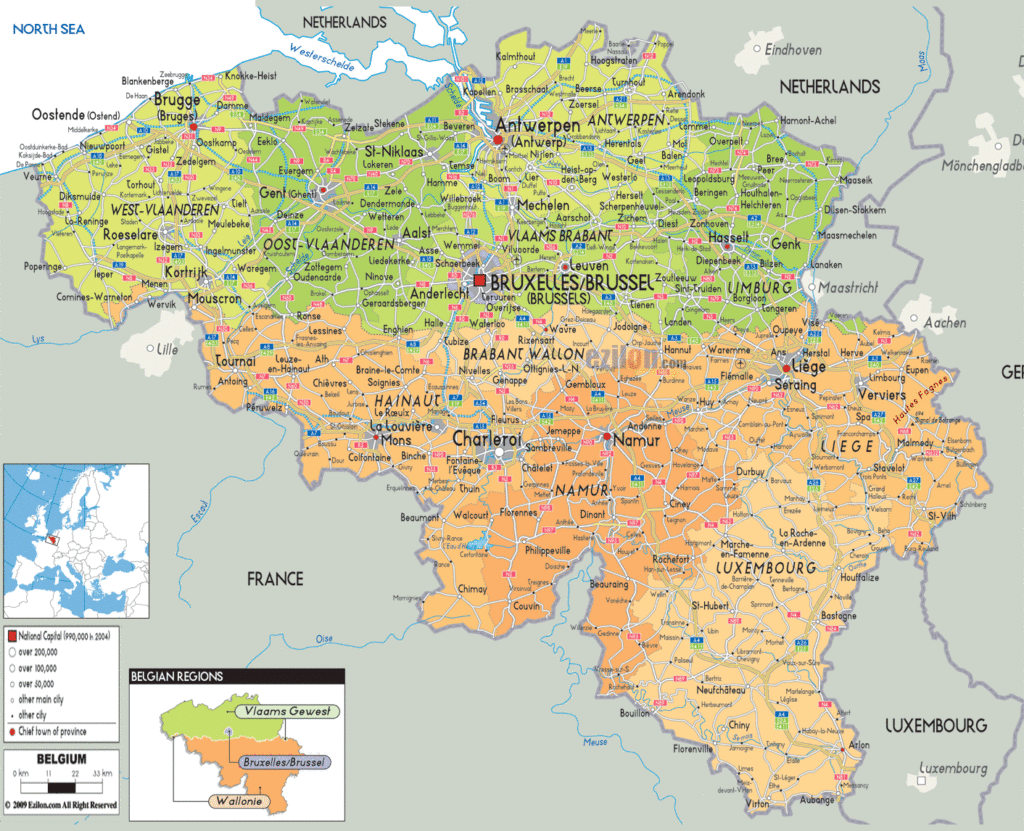
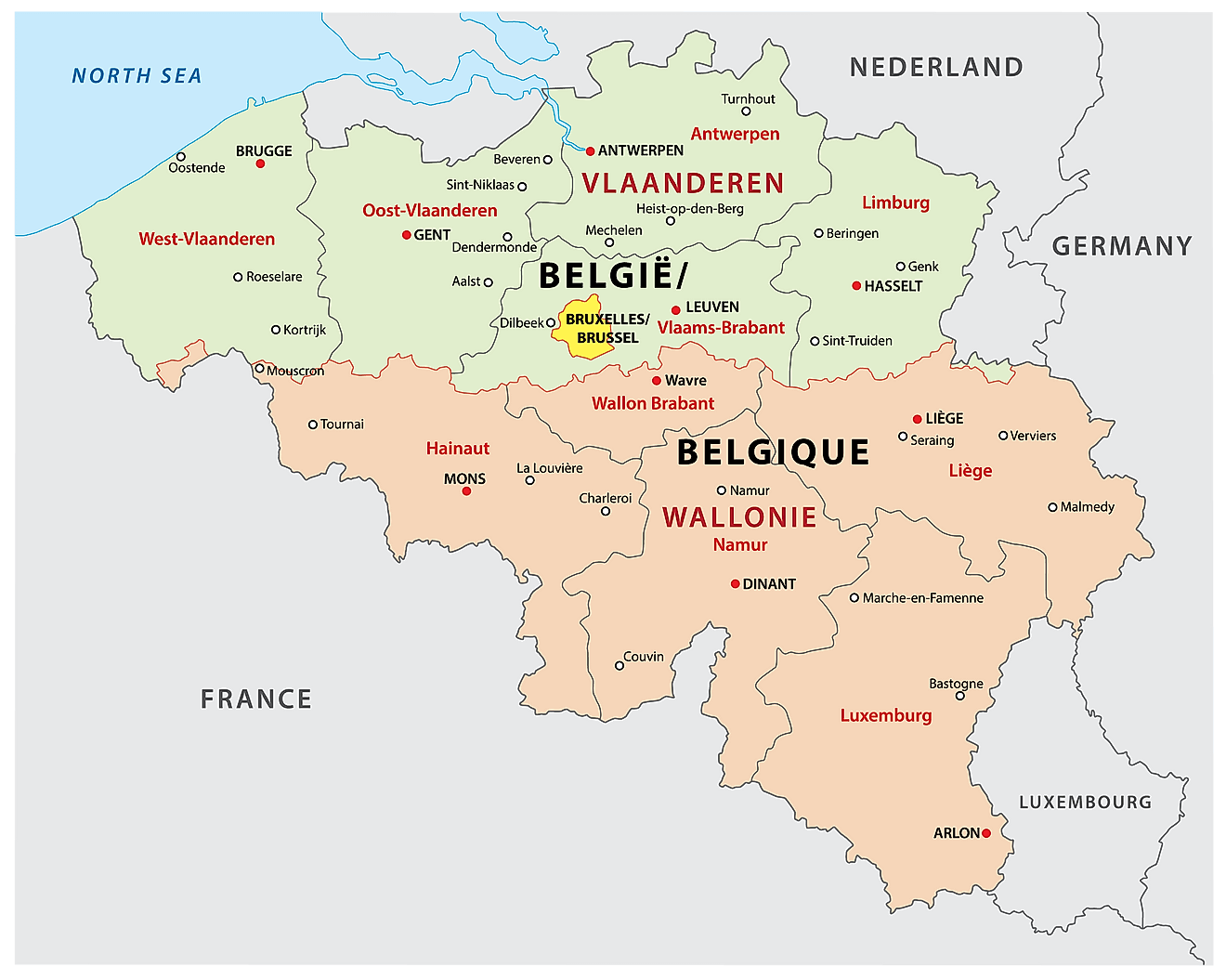
Belgium (officially, the Kingdom of Belgium) is a federal state divided into three regions. These are Flemish Regions/Flanders, Wallonia/Walloon Region and the Brussels Capital Region. The former two are subdivided into 5 provinces while the latter is remains undivided. The regions are further subdivided into 43 administrative arrondissements and then into municipalities.
With an area of 30,689 sq. km, and a population of 11.5 million residents, Belgium is the 6th most densely populated nation in Europe and the 22nd most densely populated country in the world. Located in the north-central part of the country is, Brussels – the capital, the largest and the most populous city of Belgium. It is also the de-facto capital of EU. Brussels is the administrative, financial and economic center of Belgium.
Location Maps
Where is Belgium?
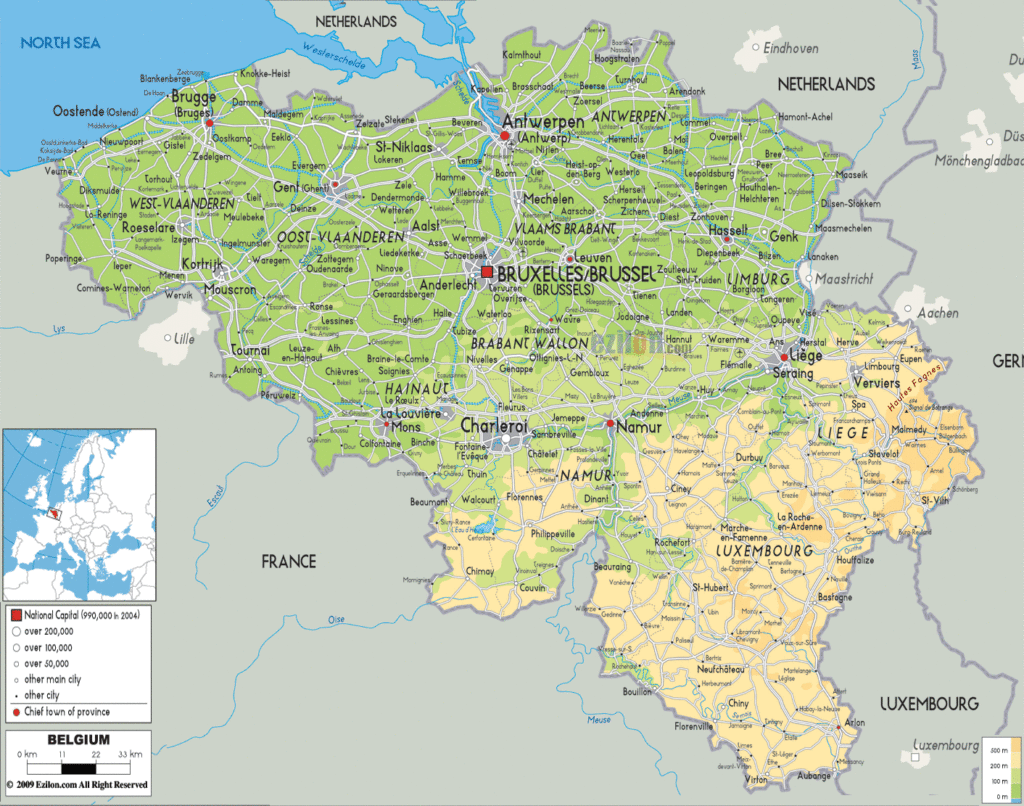
Belgium is a small and mostly low-lying country located in western Europe along the North Sea. It’s positioned between France to the south, Germany and Luxembourg to the east, as well as the Netherlands to the north. Belgium is famous for its chocolate, waffles, beer, festivals, and national football (soccer) team, known as the Red Devils.
The population is estimated to be 11 million people with one-tenth living in the capital and largest city of Brussels. This city is known for being the headquarters of the European Union, an alliance within Europe promoting free trade and economic movement.
High Definition Political Map of Belgium
History
Antiquity
France. In 870 in the Treaty of Meerssen, modern Belgium lands all became part of the western kingdom for a period, but in 880 in the Treaty of Ribemont, Lotharingia returned to the lasting control of the Eastern king, or Holy Roman Emperor. The lordships and bishoprics along the “March” (frontier) between the two great kingdoms maintained important connections between each other. For example, the county of Flanders expanded over the Scheldt into the empire, and during several periods was ruled by the same lords as the county of Hainaut.
In the 13th and 14th centuries, the cloth industry and commerce boomed especially in the County of Flanders and it became one of the richest areas in Europe. This prosperity played a role in conflicts between Flanders and the king of France. Famously, Flemish militias scored a surprise victory at the Battle of the Golden Spurs against a strong force of mounted knights in 1302, but France soon regained control of the rebellious province.
Burgundian and Habsburg Netherlands
In the 15th century, the Duke of Burgundy in France took control of Flanders, and from there they proceeded to unite much of what is now the Benelux, the so-called Burgundian Netherlands. “Burgundy” and “Flanders” were the first two common names used for the Burgundian Netherlands which was the predecessor of the Austrian Netherlands, the predecessor of modern Belgium. The union, technically stretching between two kingdoms, gave the area economic and political stability which led to an even greater prosperity and artistic creation.
Born in Belgium, the Habsburg Emperor Charles V was heir of the Burgundians, but also of the royal families of Austria, Castile and Aragon. With the Pragmatic Sanction of 1549 he gave the Seventeen Provinces more legitimacy as a stable entity, rather than just a temporary personal union. He also increased the influence of these Netherlands over the Prince-Bishopric of Liège, which continued to exist as a large semi-independent enclave.
Spanish and Austrian Netherlands
The Eighty Years’ War (1568–1648) was triggered by the Spanish government’s policy towards Protestantism, which was becoming popular in the Low Countries. The rebellious northern United Provinces (Belgica Foederata in Latin, the “Federated Netherlands”) eventually separated from the Southern Netherlands (Belgica Regia, the “Royal Netherlands”). The southern part continued to be ruled successively by the Spanish (Spanish Netherlands) and the Austrian House of Habsburgs (Austrian Netherlands) and comprised most of modern Belgium. This was the theatre of several more protracted conflicts during much of the 17th and 18th centuries involving France, including the Franco-Dutch War (1672–1678), the Nine Years’ War (1688–1697), the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–1714), and part of the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748).
The French revolution and the Kingdom of the Netherlands
Following the campaigns of 1794 in the French Revolutionary Wars, the Low Countries – including territories that were never nominally under Habsburg rule, such as the Prince-Bishopric of Liège – were annexed by the French First Republic, ending Austrian rule in the region. A reunification of the Low Countries as the United Kingdom of the Netherlands occurred at the dissolution of the First French Empire in 1814, after the abdication of Napoleon.
Independent Belgium
In 1830, the Belgian Revolution led to the re-separation of the Southern Provinces from the Netherlands and to the establishment of a Catholic and bourgeois, officially French-speaking and neutral, independent Belgium under a provisional government and a national congress. Since the installation of Leopold I as king on 21 July 1831, now celebrated as Belgium’s National Day, Belgium has been a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy, with a laicist constitution based on the Napoleonic code. Although the franchise was initially restricted, universal suffrage for men was introduced after the general strike of 1893 (with plural voting until 1919) and for women in 1949.
The main political parties of the 19th century were the Catholic Party and the Liberal Party, with the Belgian Labour Party emerging towards the end of the 19th century. French was originally the official language used by the nobility and the bourgeoisie, especially after the rejection of the Dutch monarchy. French progressively lost its dominance as Dutch began to recover its status. This recognition became official in 1898, and in 1967, the parliament accepted a Dutch version of the Constitution.
The Berlin Conference of 1885 ceded control of the Congo Free State to King Leopold II as his private possession. From around 1900 there was growing international concern for the extreme and savage treatment of the Congolese population under Leopold II, for whom the Congo was primarily a source of revenue from ivory and rubber production. Many Congolese were killed by Leopold’s agents for failing to meet production quotas for ivory and rubber. In 1908, this outcry led the Belgian state to assume responsibility for the government of the colony, henceforth called the Belgian Congo. A Belgian commission in 1919 estimated that Congo’s population was half what it was in 1879.
Germany invaded Belgium in August 1914 as part of the Schlieffen Plan to attack France, and much of the Western Front fighting of World War I occurred in western parts of the country. The opening months of the war were known as the Rape of Belgium due to German excesses. Belgium assumed control of the German colonies of Ruanda-Urundi (modern-day Rwanda and Burundi) during the war, and in 1924 the League of Nations mandated them to Belgium. In the aftermath of the First World War, Belgium annexed the Prussian districts of Eupen and Malmedy in 1925, thereby causing the presence of a German-speaking minority.
German forces again invaded the country in May 1940, and 40,690 Belgians, over half of them Jews, were killed during the subsequent occupation and the Holocaust. From September 1944 to February 1945 the Allies liberated Belgium. After World War II, a general strike forced King Leopold III to abdicate in 1951 in favour of his son, Prince Baudouin, since many Belgians felt he had collaborated with Germany during the war. The Belgian Congo gained independence in 1960 during the Congo Crisis; Ruanda-Urundi followed with its independence two years later. Belgium joined NATO as a founding member and formed the Benelux group of nations with the Netherlands and Luxembourg.
Belgium became one of the six founding members of the European Coal and Steel Community in 1951 and of the European Atomic Energy Community and European Economic Community, established in 1957. The latter has now become the European Union, for which Belgium hosts major administrations and institutions, including the European Commission, the Council of the European Union and the extraordinary and committee sessions of the European Parliament.
In the early 1990s, Belgium saw several large corruption scandals notably surrounding Marc Dutroux, Andre Cools, the Dioxin Affair, Agusta Scandal and the murder of Karel van Noppen.
Physical Map of Belgium
Geography
Belgium shares borders with France (620 km), Germany (167 km), Luxembourg (148 km) and the Netherlands (450 km). Its total surface, including water area, is 30,528 km (11,787 sq mi). Before 2018, its total area was believed to be 30,528 km (11,787 sq mi). However, when the country’s statistics were measured in 2018, a new calculation method was used. Unlike previous calculations, this one included the area from the coast to the low-water line, revealing the country to be 160 km (62 sq mi) larger in surface area than previously thought. Its land area alone is 30,278 km. It lies between latitudes 49°30′ and 51°30′ N, and longitudes 2°33′ and 6°24′ E.
Belgium has three main geographical regions; the coastal plain in the northwest and the central plateau both belong to the Anglo-Belgian Basin, and the Ardennes uplands in the southeast to the Hercynian orogenic belt. The Paris Basin reaches a small fourth area at Belgium’s southernmost tip, Belgian Lorraine.
The coastal plain consists mainly of sand dunes and polders. Further inland lies a smooth, slowly rising landscape irrigated by numerous waterways, with fertile valleys and the northeastern sandy plain of the Campine (Kempen). The thickly forested hills and plateaus of the Ardennes are more rugged and rocky with caves and small gorges. Extending westward into France, this area is eastwardly connected to the Eifel in Germany by the High Fens plateau, on which the Signal de Botrange forms the country’s highest point at 694 m (2,277 ft).
The climate is maritime temperate with significant precipitation in all seasons (Köppen climate classification: Cfb), like most of northwest Europe. The average temperature is lowest in January at 3 °C (37.4 °F) and highest in July at 18 °C (64.4 °F). The average precipitation per month varies between 54 mm (2.1 in) for February and April, to 78 mm (3.1 in) for July. Averages for the years 2000 to 2006 show daily temperature minimums of 7 °C (44.6 °F) and maximums of 14 °C (57.2 °F) and monthly rainfall of 74 mm (2.9 in); these are about 1 °C and nearly 10 millimetres above last century’s normal values, respectively.
Phytogeographically, Belgium is shared between the Atlantic European and Central European provinces of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature, the territory of Belgium belongs to the terrestrial ecoregions of Atlantic mixed forests and Western European broadleaf forests. Belgium had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 1.36/10, ranking it 163rd globally out of 172 countries.
Provinces
The territory of Belgium is divided into three Regions, two of which, the Flemish Region and Walloon Region, are in turn subdivided into provinces; the third Region, the Brussels Capital Region, is neither a province nor a part of a province.