The Faroe Islands (/ˈfɛəroʊ/ FAIR-oh), or simply the Faroes (Faroese: Føroyar [ˈfœɹjaɹ] (listen); Danish: Færøerne [ˈfeɐ̯ˌøˀɐnə]), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located 320 kilometres (200 mi) north-northwest of the United Kingdom, and about halfway between Norway (580 kilometres (360 mi) away) and Iceland (430 kilometres (270 mi) away). The islands form part of the Kingdom of Denmark, along with mainland Denmark and Greenland. The islands have a total area of about 1,400 square kilometres (540 sq mi) with a population of 54,000 as of June 2022.
The terrain is rugged, and the subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc) is windy, wet, cloudy, and cool. Temperatures for such a northerly climate are moderated by the Gulf Stream, averaging above freezing throughout the year, and hovering around 12 °C (54 °F) in summer and 5 °C (41 °F) in winter. The northerly latitude also results in perpetual civil twilight during summer nights and very short winter days.
Between 1035 and 1814, the Faroe Islands were part of the Kingdom of Norway, which was in a personal union with Denmark from 1380. In 1814, the Treaty of Kiel transferred Norway to Sweden, whereas Denmark kept its Atlantic territories, which included the Faroe Islands, Greenland and Iceland.
While part of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Faroe Islands have been self-governing since 1948, controlling most areas apart from military defence, policing, justice, currency, and foreign affairs. Because the Faroe Islands are not part of the same customs area as Denmark, the Faroe Islands have an independent trade policy, and can establish trade agreements with other states. The Faroes have an extensive bilateral free trade agreement with Iceland, known as the Hoyvík Agreement. In the Nordic Council, they are represented as part of the Danish delegation. In certain sports, the Faroe Islands field their own national teams. They did not become a part of the European Economic Community in 1973, instead keeping the autonomy over their own fishing waters.
| Capital Value: | Tórshavn |
|---|---|
| Official languages: |
|
| Demonym(s): |
|
| Government: | Devolved government within a parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Legislature: | Løgting |
| Density: | 38.6/km (100.0/sq mi) |
| Currency Value: | Faroese króna (DKK) |
| Driving side: | right |
| Calling code: | +298 |
| Internet TLD: | .fo |
Location Maps
Where is Faroe Islands?
High Definition Political Map of Faroe Islands
History
There is some evidence of settlement on the Faroe Islands before Norse Viking settlers arrived in the ninth century AD. Archeologists found burnt grains of domesticated barley and peat ash deposited in two phases; the first dated between the mid-fourth and mid-sixth centuries, and another between the late-sixth and late-eighth centuries. Researchers have also found sheep DNA in lake-bed sediments, which were dated to around the year 500. Barley and sheep had to have been brought to the islands by humans. As Scandinavians did not begin using the sail until about 750, it is unlikely they could have reached the Faroes before then, and it is more likely the settlers came from Great Britain or Ireland.
Archaeologist Mike Church noted that Dicuil, an Irish monk of the early ninth century, may have mentioned the Faroes. Dicuil wrote in his geographical work De mensura orbis terrae that there were heremitae ex nostra Scotia (“hermits from our land of Ireland/Scotland”) who had lived on the northerly islands of Britain for almost a hundred years until the Vikings arrived. Church suggested that the people living there might have been from Ireland, Scotland, or Scandinavia, or possibly from all three. According to a ninth-century voyage tale, the Irish saint Brendan visited islands resembling the Faroes in the sixth century. This association, however, is not conclusive.
Norsemen settled the islands c. 800, bringing Old West Norse, which evolved into the modern Faroese language. According to Icelandic sagas such as Færeyjar Saga, one of the best known men in the island was Tróndur í Gøtu, a descendant of Scandinavian chiefs who had settled in Dublin, Ireland. Tróndur led the battle against Sigmund Brestisson, the Norwegian monarchy and the Norwegian church.
The Norse and Norse–Gael settlers probably did not come directly from Scandinavia, but rather from Norse communities surrounding the Irish Sea, Northern Isles, and Outer Hebrides of Scotland, including the Shetland and Orkney islands. A traditional name for the islands in Irish, Na Scigirí, possibly refers to the (Eyja-)Skeggjar “(Island-)Beards”, a nickname given to island dwellers.
According to the Færeyinga saga, more emigrants left Norway who did not approve of the monarchy of Harald Fairhair (ruled c. 872 to 930). These people settled the Faroes around the end of the ninth century. Early in the eleventh century, Sigmundur Brestisson (961–1005) – whose clan had flourished in the southern islands before invaders from the northern islands almost exterminated it – escaped to Norway. He was sent back to take possession of the islands for Olaf Tryggvason, King of Norway from 995 to 1000. Sigmundur introduced Christianity, forcing Tróndur í Gøtu to convert or face beheading and, although Sigmundur was subsequently murdered, Norwegian taxation was upheld. Norwegian control of the Faroes continued until 1814, although, when the Kingdom of Norway (872–1397) entered the Kalmar Union with Denmark, this gradually resulted in Danish control of the islands. The Protestant Reformation in the form of Lutheranism reached the Faroes in 1538. When the union between Denmark and Norway was dissolved as a result of the Treaty of Kiel in 1814, Denmark retained possession of the Faroe Islands (along with Greenland and Iceland); Norway itself was joined in a union with Sweden.
Following the turmoil caused by the Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815), in 1816, the Faroe Islands became a county within the Danish Kingdom.
As part of its mercantilist economic policy, Denmark maintained a monopoly over trade with the Faroe Islands and forbade their inhabitants trading with others (e.g. the geographically close Britain). The trade monopoly in the Faroe Islands was abolished in 1856, after which the area developed as a modern fishing nation with its own fishing fleet. The national awakening from 1888 initially arose from a struggle to maintain the Faroese language and was thus culturally oriented, but after 1906 it became more political with the foundation of political parties within the Faroe Islands.
In the first year of the Second World War, on 12 April 1940, British troops occupied the Faroe Islands in Operation Valentine. Nazi Germany had invaded Denmark and commenced the invasion of Norway on 9 April 1940 under Operation Weserübung. In 1942–1943, the British Royal Engineers, under the command of lieutenant colonel William Law, built the first and only airport in the Faroe Islands, Vágar Airport. Following the war, control of the islands reverted to Denmark, but Danish rule had been undermined, and Iceland‘s full independence served as a precedent and a model in the mind of many Faroese.
The 1946 Faroese independence referendum resulted in 50.73% in favour of independence to 49.27% against. The Faroe Islands subsequently declared independence on 18 September 1946; however, this declaration was annulled by Denmark on 20 September on the grounds that a majority of the Faroese voters had not supported independence and King Christian X of Denmark dissolved the Faroese Løgting on 24 September. The dissolution of the Løgting took place in November, followed by the Faroese parliamentary election of 1946 in which the parties in favour of full independence received a total of 5,396 votes while the parties opposed to it received a total of 7,488 votes. As a reaction to the growing movements in favour of self-government and independence, Denmark finally granted the Faroe Islands home-rule with a high degree of local autonomy in 1948.
In 1973 the Faroe Islands declined to join Denmark in entering the European Economic Community (which later became the European Union). Following the collapse of the fishing industry in the early 1990s, the Faroes experienced considerable economic difficulties.
Geography
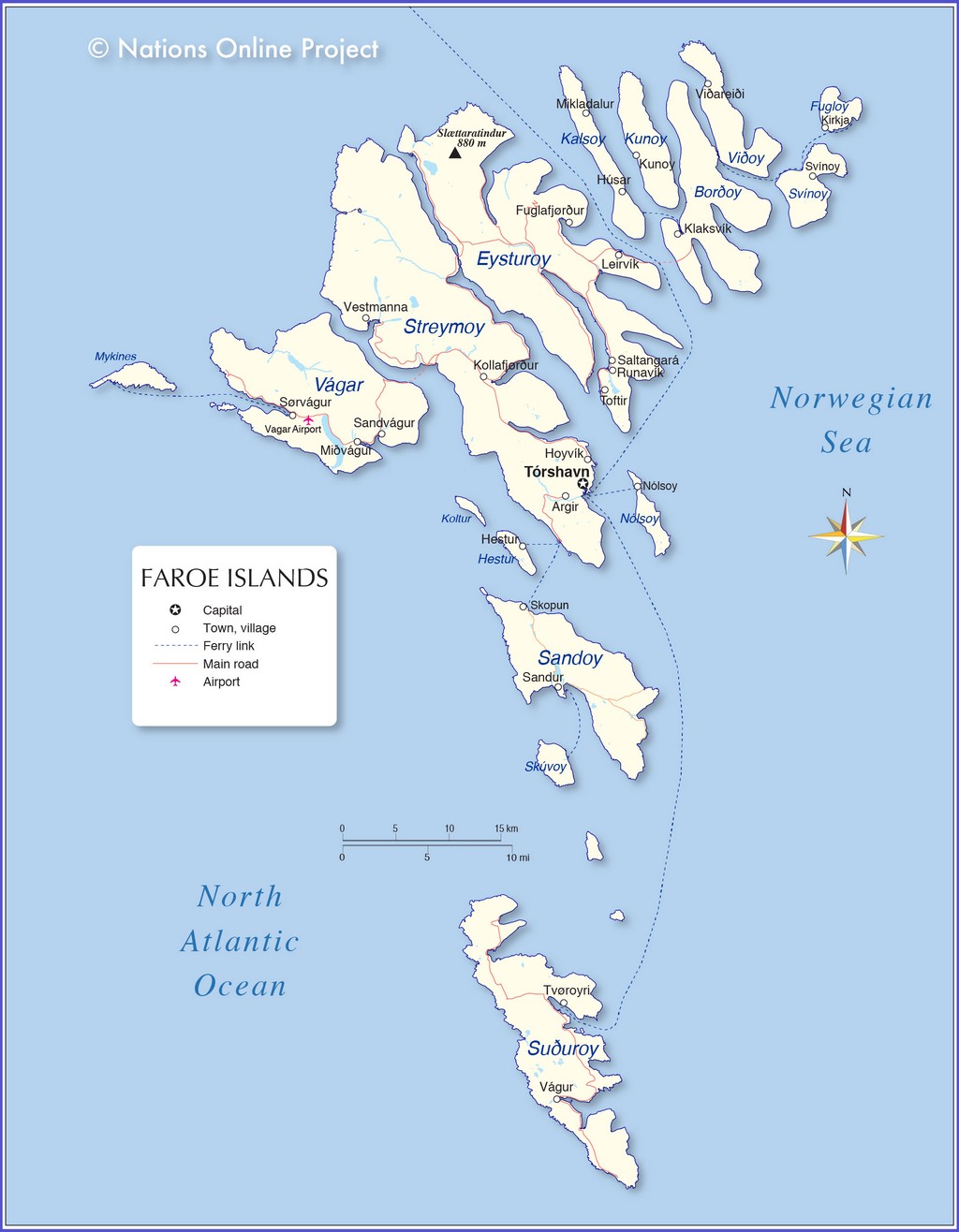
The Faroe Islands are an island group consisting of 18 major islands (and a total of 779 islands, islets, and skerries) about 655 kilometres (407 mi) off the coast of Northern Europe, between the Norwegian Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, about halfway between Iceland and Norway, the closest neighbours being the Northern Isles and the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. Its coordinates are 62°00′N 06°47′W / 62.000°N 6.783°W / 62.000; -6.783.
Distance from the Faroe Islands to:
- Rona, Scotland (uninhabited): 260 kilometres (160 mi)
- Shetland (Foula), Scotland: 285 kilometres (177 mi)
- Orkney (Westray), Scotland: 300 kilometres (190 mi)
- Scotland (mainland): 320 kilometres (200 mi)
- Iceland: 450 kilometres (280 mi)
- Norway: 590 kilometres (370 mi)
- Ireland: 670 kilometres (420 mi)
- Denmark: 990 kilometres (620 mi)
The islands cover an area of 1,399 square kilometres (540 sq. mi) and have small lakes and rivers, but no major ones. There are 1,117 kilometres (694 mi) of coastline. The only significant uninhabited island is Lítla Dímun.
The islands are rugged and rocky with some low peaks; the coasts are mostly cliffs. The highest point is Slættaratindur in northern Eysturoy, 882 metres (2,894 ft) above sea level.
The Faroe Islands are made up of an approximately six-kilometres-thick succession of mostly basaltic lava that was part of the great North Atlantic Igneous Province during the Paleogene period. The lavas were erupted during the opening of the North Atlantic ocean, which began about 60 million years ago, and what is today the Faroe Islands was then attached to Greenland. The lavas are underlain by circa 30 km of unidentified ancient continental crust.
Climate
The climate is classed as subpolar oceanic climate according to the Köppen climate classification: Cfc, with areas having a tundra climate, especially in the mountains, although some coastal or low-lying areas may have very mild-winter versions of a tundra climate. The overall character of the climate of the islands is influenced by the strong warming influence of the Atlantic Ocean, which produces the North Atlantic Current. This, together with the remoteness of any source of landmass-induced warm or cold airflows, ensures that winters are mild (mean temperature 3.0 to 4.0 °C or 37 to 39 °F) while summers are cool (mean temperature 9.5 to 10.5 °C or 49 to 51 °F).
The islands are windy, cloudy, and cool throughout the year with an average of 210 rainy or snowy days per year. The islands lie in the path of depressions moving northeast, making strong winds and heavy rain possible at all times of the year. Sunny days are rare and overcast days are common. Hurricane Faith struck the Faroe Islands on 5 September 1966 with sustained winds over 100 mph (160 km/h) and only then did the storm cease to be a tropical system.
The climate varies greatly over small distances, due to the altitude, ocean currents, topography, and winds. Precipitation varies considerably throughout the archipelago. In some highland areas, snow cover may last for months with snowfalls possible for the greater part of the year (on the highest peaks, summer snowfall is by no means rare), while in some sheltered coastal locations, several years pass without any snowfall whatsoever. Tórshavn receives frosts more often than other areas just a short distance to the south. Snow also is seen at a much higher frequency than on outlying islands nearby. The area receives on average 49 frosts a year.
The collection of meteorological data on the Faroe Islands began in 1867. Winter recording began in 1891, and the warmest winter occurred in 2016–17 with an average temperature of 6.1 °C (43 °F).
The Faroes belong to the Faroe Islands boreal grasslands ecoregion. The natural vegetation of the Faroe Islands is dominated by arctic-alpine plants, wildflowers, grasses, moss, and lichen. Most of the lowland area is grassland and some is heath, dominated by shrubby heathers, mainly Calluna vulgaris. Among the herbaceous flora that occur in the Faroe Islands is the cosmopolitan marsh thistle, Cirsium palustre.
Although there are no trees native to the Faroe Islands, a limited number of species have been successfully introduced to the region, in particular trees from the Magellanic subpolar forests region of Chile. Conditions in the Magellanic subpolar forests are similar to those in the Faroe Islands, with cold summers and near-continuous subpolar winds. The following species from Tierra del Fuego, Drimys winteri, Nothofagus antarctica, Nothofagus pumilio, and Nothofagus betuloides, have been successfully introduced to the Faroe Islands. A non-Chilean species that has been introduced is the black cottonwood, also known as the California poplar (Populus trichocarpa).
A collection of Faroese marine algae resulting from a survey sponsored by NATO, the British Museum (Natural History) and the Carlsberg Foundation, is preserved in the Ulster Museum (catalogue numbers: F3195–F3307). It is one of ten exsiccatae sets. A few small plantations consisting of plants collected from similar climates such as Tierra del Fuego in South America and Alaska thrive on the islands.
The bird fauna of the Faroe Islands is dominated by seabirds and birds attracted to open land such as heather, probably because of the lack of woodland and other suitable habitats. Many species have developed special Faroese sub-species: common eider, Common starling, Eurasian wren, common murre, and black guillemot. The pied raven, a colour morph of the North Atlantic subspecies of the common raven, was endemic to the Faroe Islands, but now has become extinct.
Only a few species of wild land mammals are found in the Faroe Islands today, all introduced by humans. Three species are thriving on the islands today: mountain hare (Lepus timidus), brown rat (Rattus norvegicus), and the house mouse (Mus musculus). Apart from these, there is a local domestic sheep breed, the Faroe sheep (depicted on the coat of arms), and there once was a variety of feral sheep, which survived on Lítla Dímun until the mid-nineteenth century.
Grey seals (Halichoerus grypus) are common around the shorelines. Several species of cetacea live in the waters around the Faroe Islands. Best known are the long-finned pilot whales (Globicephala melaena), which still are hunted by the islanders in accordance with longstanding local tradition. Orcas (Orcinus orca) are regular visitors around the islands.
The domestic animals of the Faroe Islands are a result of 1,200 years of isolated breeding. As a result, many of the islands’ domestic animals are found nowhere else in the world. Faroese domestic breeds include Faroe pony, Faroe cow, Faroe sheep, Faroese goose, and Faroese duck.
Geology
The islands were built up during a period characterised by high volcanic activity in the Early Palaeogene around 50-60 million years ago. The islands are built up in layers of different lava flows (basalt) alternating with thin layers of volcanic ash (tuff). The soft ash and the hard basalt thus lie layer upon layer in narrow and thick strips. The soft tuff or ash zones erode away relatively quickly, and the hard lump of basalt above the eroded tuff falls away, forming the first terrace.
Volcanic activity has varied over millions of years, with periods of quiescence and various periods of quiet eruptive fissures and explosive volcanism. In a few places, mainly on Suðuroy, thin layers of coal are present, which are the remains of swamp forests from the time between volcanic eruptions. The plateau has therefore been divided into different basalt series according to the course of volcanism and the age sequence of the layers.
There are major differences in the shape of the islands’ terraces. The lowest and oldest series are thick lava deposits that can be seen on the southern part of Suðuroy, Mykines, Tindhólmur and the western side of Vágar. The basalts of the lower basalt series are often pillared, which is shown by elongated, angular and regular pillars in the mountain side. Very regular vertical columns are found on northern Mykines, where they can be up to 30 metres (98 ft) high.
The middle basalt series consists of thin lava flows with a highly porous interlayer. This series has very little resistance to crumbling and weathering. As these erosion processes are more severe at higher altitudes than lower down, the lowlands are filled with weathering material from the heights, often resulting in a characteristic curved landscape shape. This can be clearly seen on Vágar, the northernmost part of Streymoy and on the north-western part of Eysturoy.
Glacial activity has reduced plateau surfaces, especially on the northern islands, where the surfaces have been reduced to a series of narrower or wider zig-zag rows along the length of the islands. The phenomenon is particularly pronounced on the islands of Kunoy, Kalsoy and Borðoy, where an eastward and a westward ice mass have eroded the intervening mountain range into a narrow ridge.