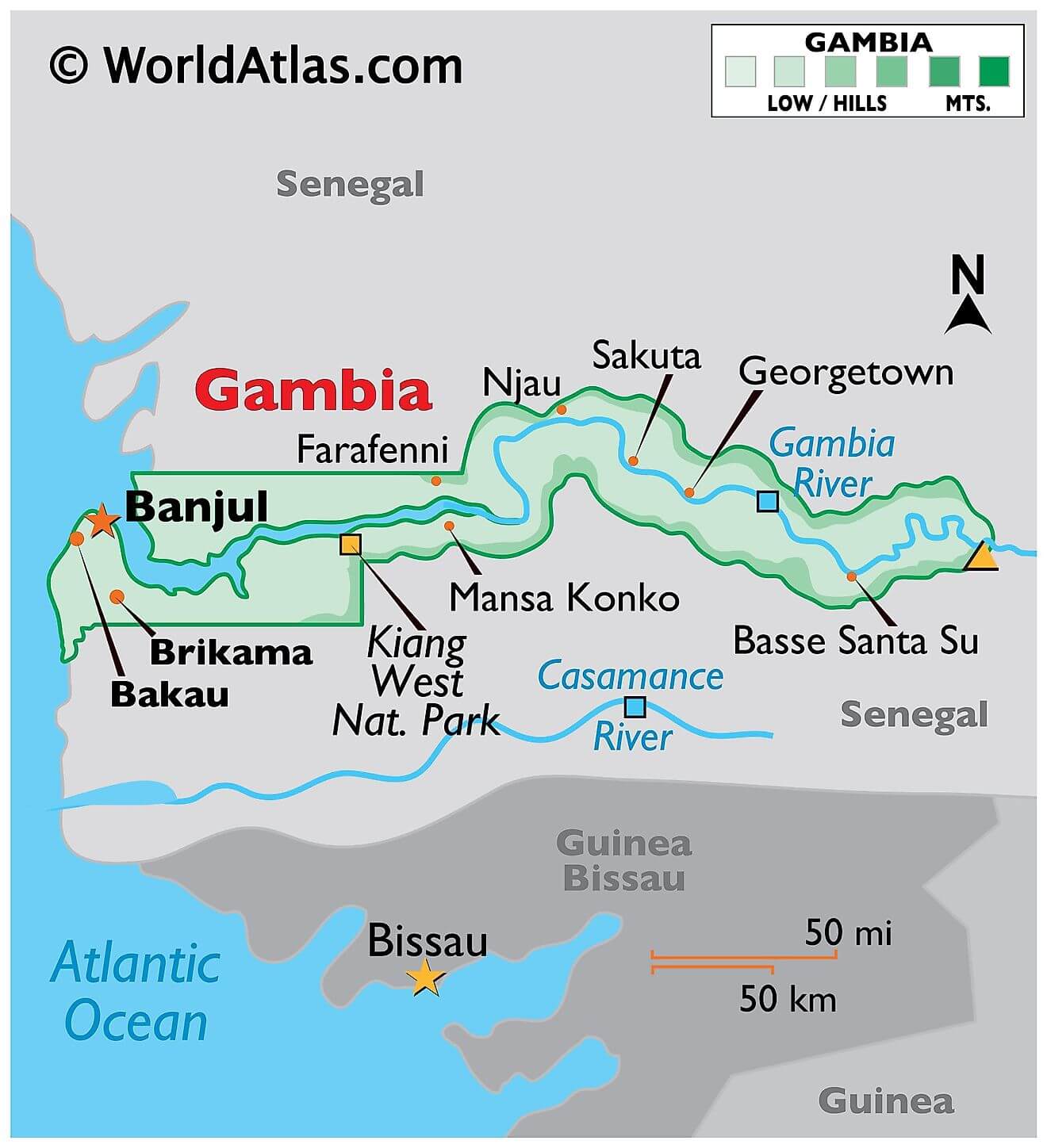
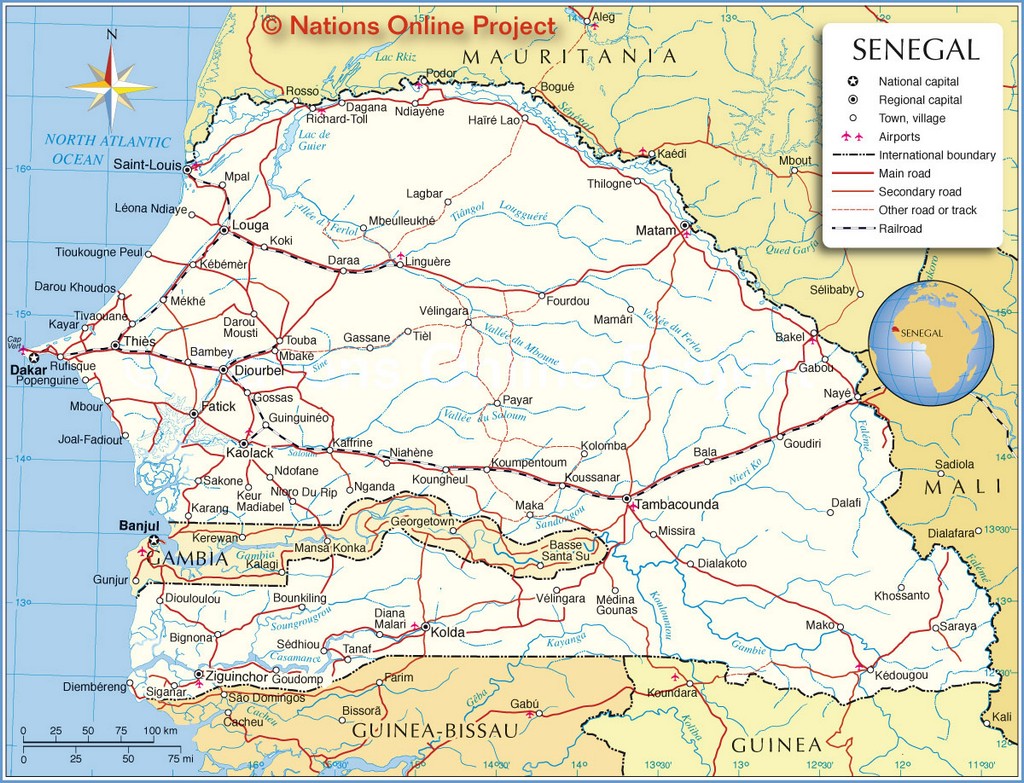
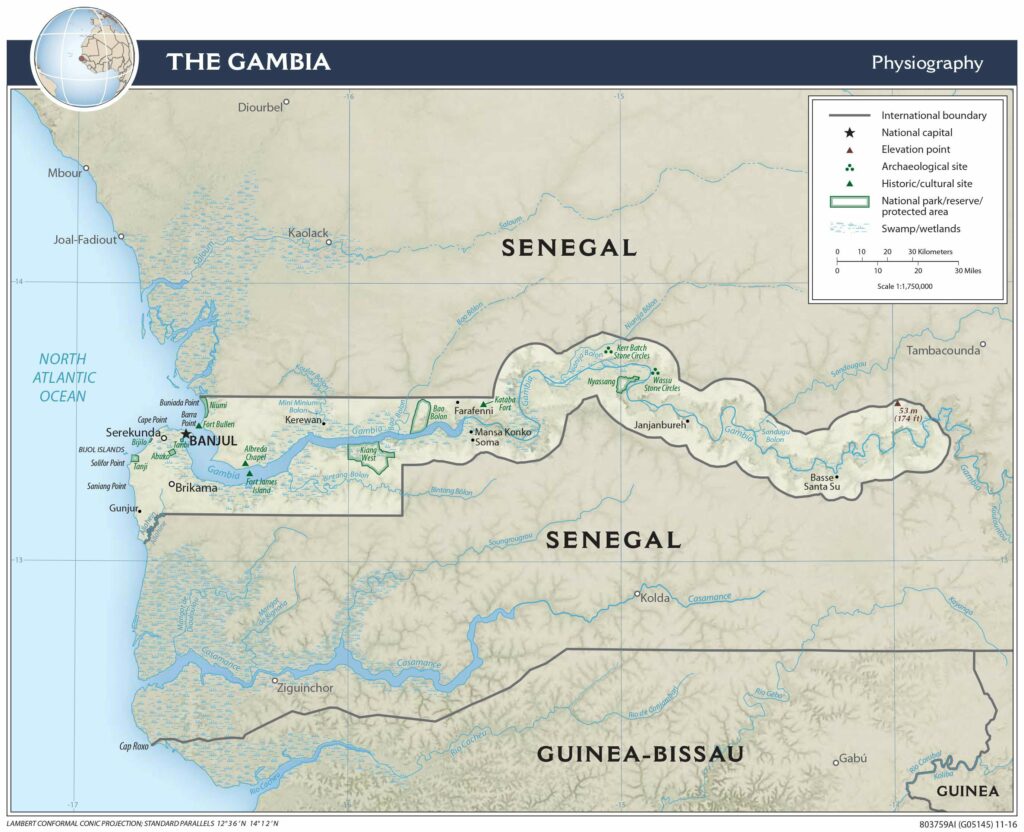
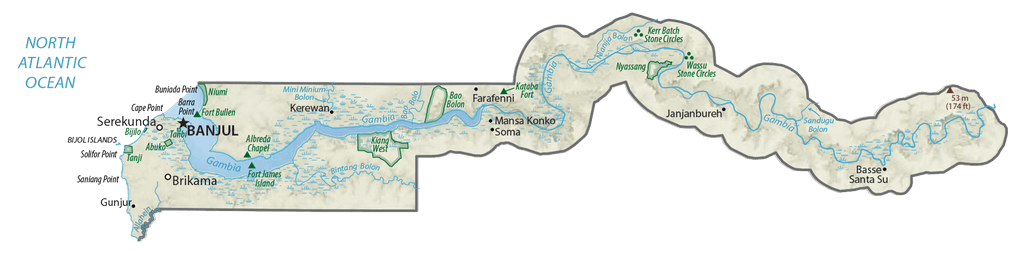
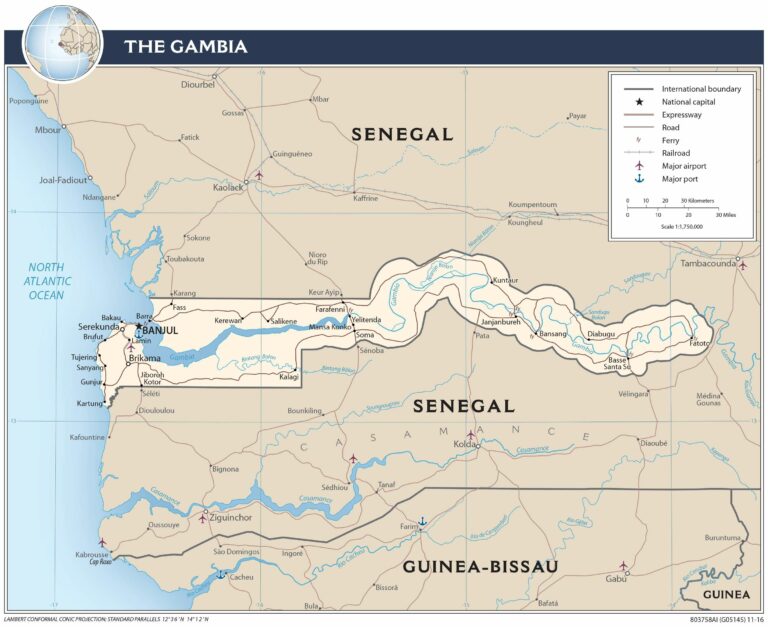
As observed on the physical map of the country, The Gambia is a very small and narrow country whose borders seem to follow the path of the meandering Gambia River, and at less than 30 miles wide at its widest point, nearly 10% of the country’s land area is covered by water.
The Gambia River itself is one of Africa’s major rivers. It stretches 1,130 km (700 miles) from northwestern Guinea to the Atlantic Ocean at the city of Banjul. It is navigable for about half of that length.
The remainder of Gambia’s terrain is a grassy flood plain with Guinean mangroves covering the landscape as you move closer to the coastline; the Sudanian Savanna lies further inland.
The highest point of the country (marked with an upright yellow triangle on the map) is an unnamed hill at 53 m at the easternmost region, and the lowest point is the Atlantic Ocean (0 m).
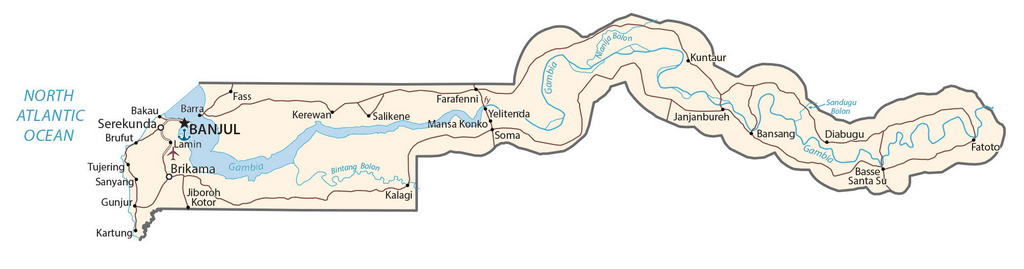
Explore the beauty and unique topography of the Gambia with this detailed map. View the country’s physical features such as the Gambia River, mountains, highways, and cities. You can also see the administrative divisions of the Gambia, with its districts outlined.
Online Interactive Political Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
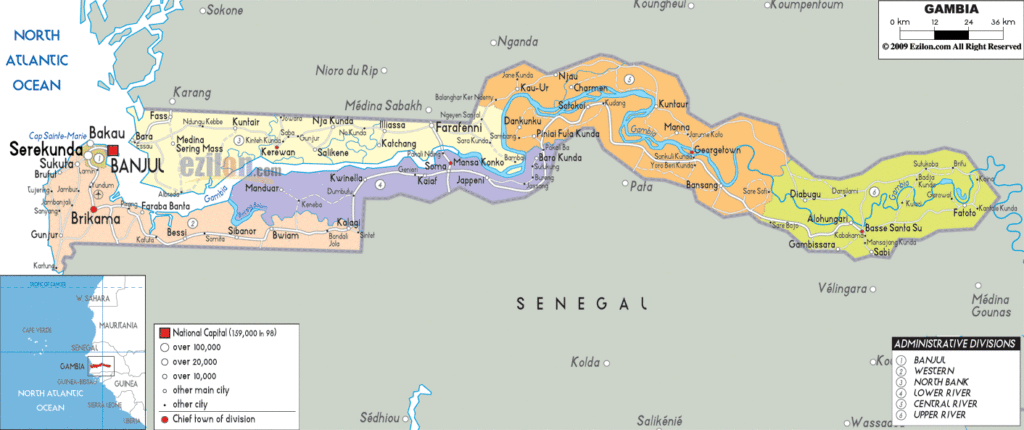
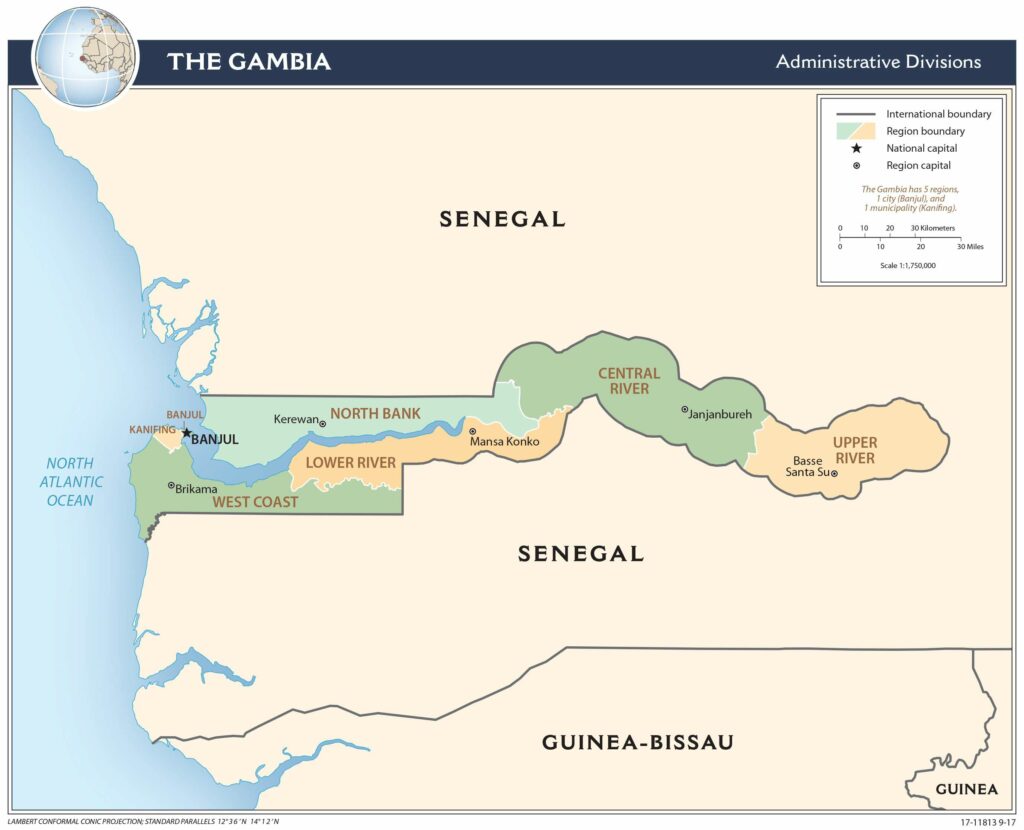
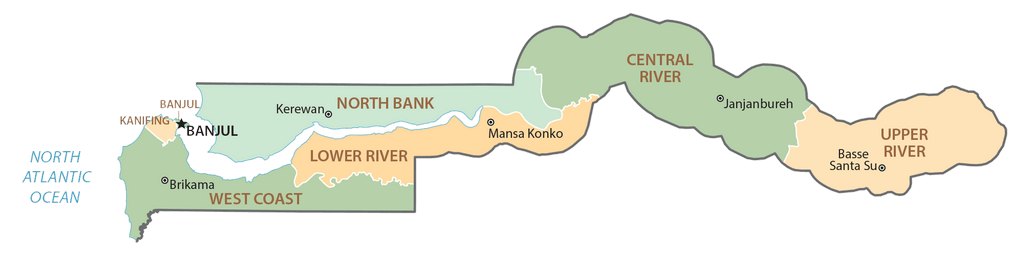
The Gambia is divided into five regions. These are Central River, Lower River, North Bank, Upper River, and West Coast. The country also has one City or Banjul which is the capital of the country. With an area of 2,894.25 sq. km, Central River is the largest region by area while the West Coast is the most populous one.
Location Maps
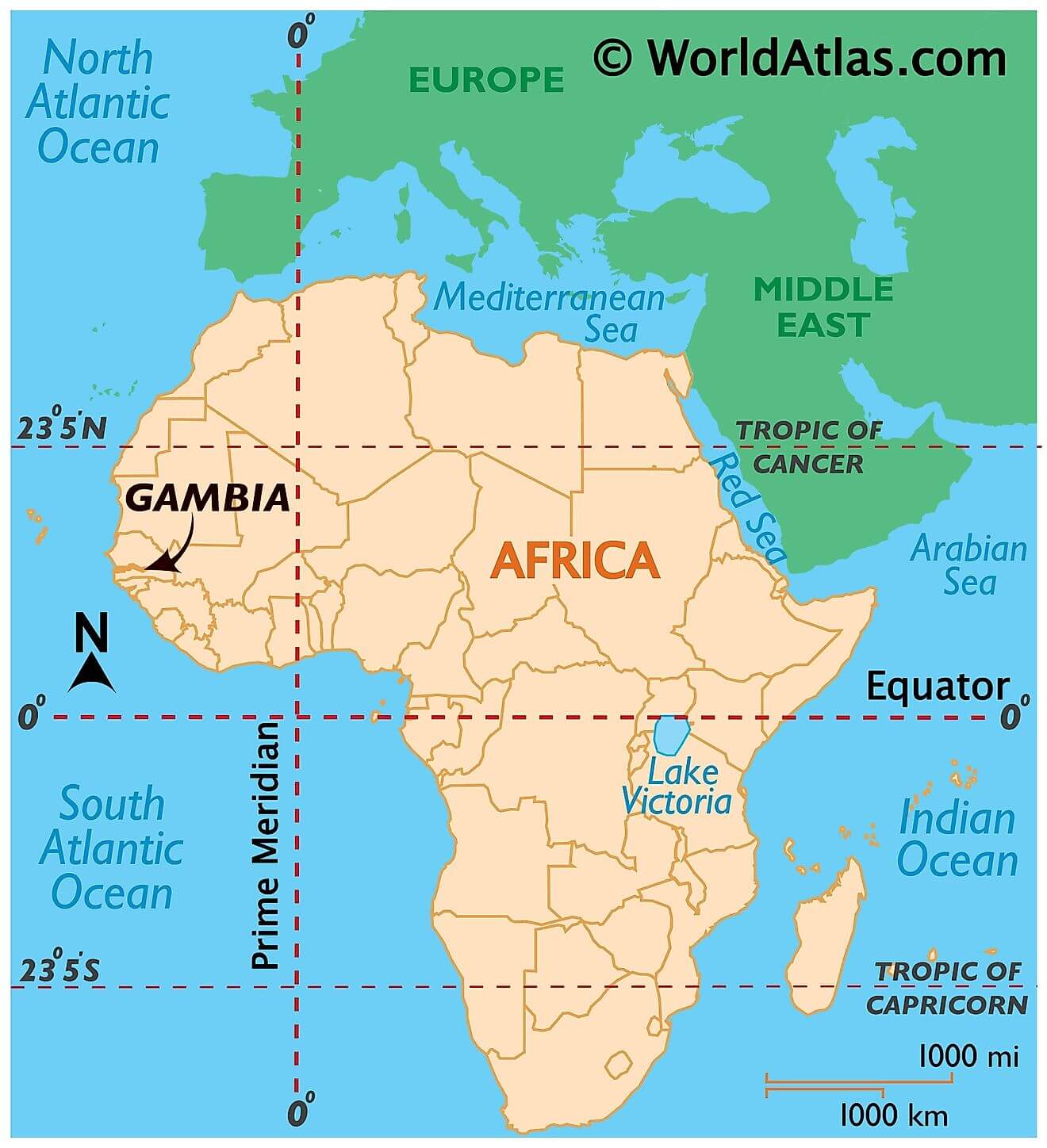
Where is Gambia?
The Gambia is the smallest country in mainland Africa, situated in Western Africa and completely surrounded by Senegal. It is known for its unique boundary, which was mostly set by a buffer of 20-30 miles along the Gambia River. It is also the only other country besides The Bahamas that formally includes “The” in its name. Geographically, The Gambia is completely surrounded by Senegal, with 80 kilometers (50 miles) of coastline on the North Atlantic Ocean.
High Definition Political Map of Gambia
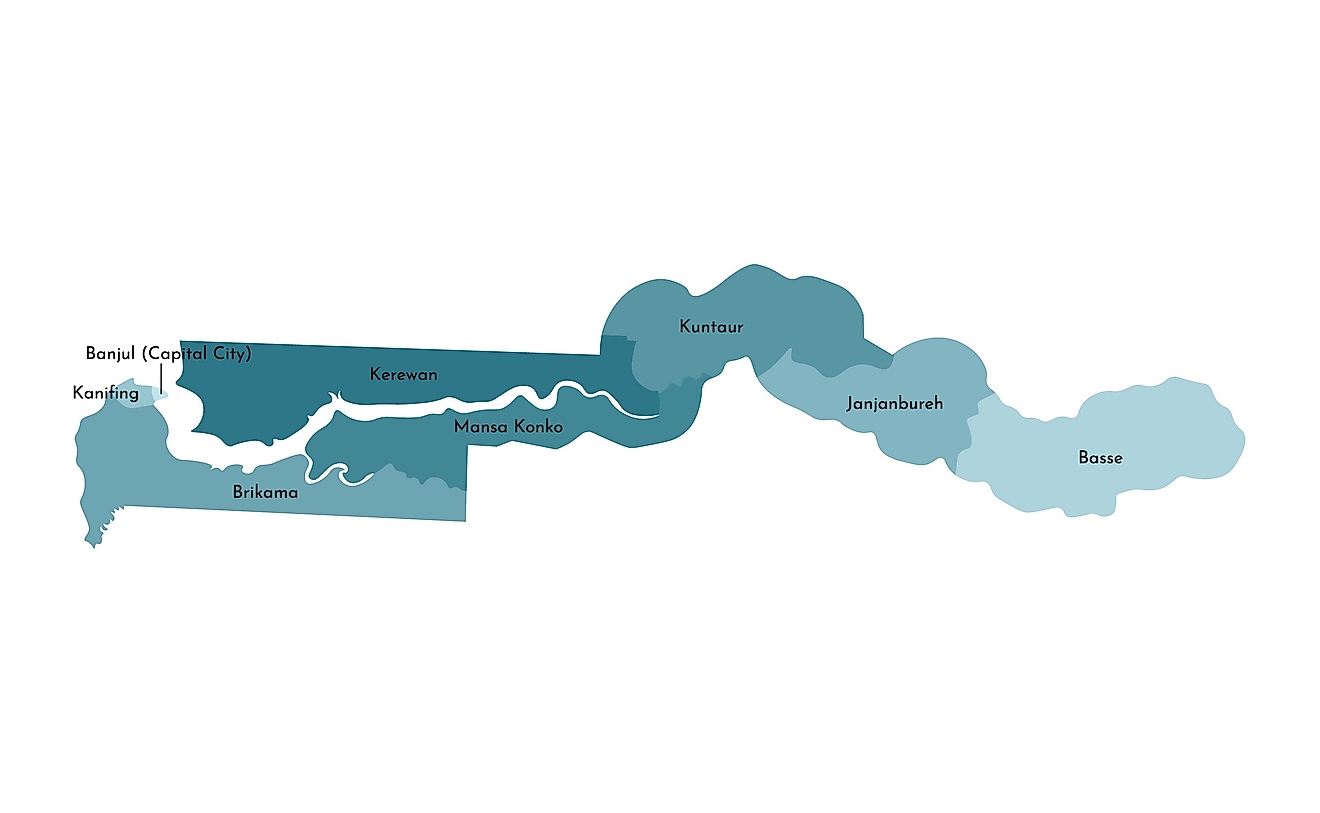
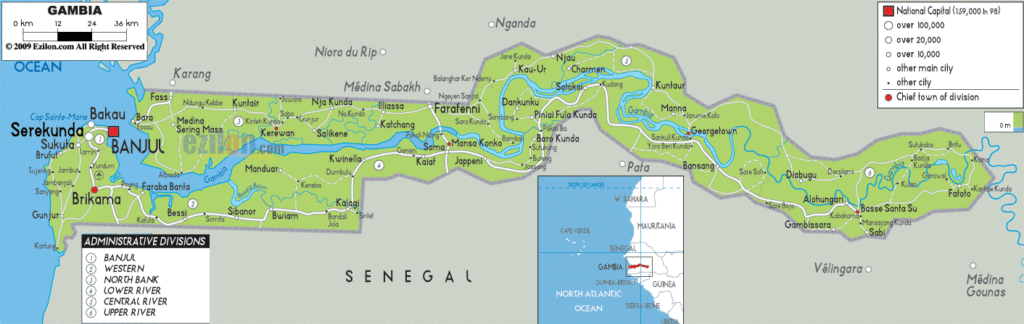
Gambia Administrative Map
History
Gambia is a small West African country, surrounded by Senegal on all sides except for a short coastline on the Atlantic Ocean. The region that is now Gambia has a long and complex history, dating back thousands of years.
The first known inhabitants of the region were the Jola people, followed by other ethnic groups such as the Mandinka, Wolof, and Fula. The region was also an important center of the transatlantic slave trade, with many thousands of enslaved Africans passing through its ports.
In the late 19th century, Gambia became a British colony, and the country remained under British rule until it gained independence in 1965. During the colonial period, the British authorities worked to suppress local customs and traditions, and imposed their own legal and administrative systems.
After independence, Gambia was ruled by Sir Dawda Jawara, who established a multi-party democracy and worked to promote economic development and social welfare. However, Jawara’s government was also marked by allegations of corruption and authoritarianism.
In 1994, Jawara was overthrown in a military coup led by Yahya Jammeh, who ruled the country for the next 22 years. Jammeh’s regime was marked by human rights abuses, including torture, extrajudicial killings, and restrictions on political opposition and the media.
In 2016, Jammeh was defeated in a presidential election by Adama Barrow, who took office in January 2017. Barrow has pledged to promote democratic reforms and to address the country’s economic and social challenges, including poverty, high unemployment, and a lack of access to healthcare and education.
Gambia is one of the smallest countries in Africa, but it has a rich cultural heritage and a diverse population. Despite its challenges, the country has made significant progress in recent years, and there is hope for a brighter future for its people.
Physical Map of Gambia